(Translated by Google) Good service and kindness Edith is a very kind person (Original) Buena atención y amabilidad Edith es una persona muy amable
Read More
TB Skin Test VS Quantiferon Blood Test
Posted: Dec 14th, 2022 at 12:00AM

A tuberculosis (TB) test checks whether you have TB bacteria in your body. Most institutions, especially within the healthcare industry, require their employees to undergo a TB test before employment, usually on an annual basis. There are two types of TB tests: skin tests and blood tests. Let's talk more about each of these individually, how they work, and what the benefits are.
TB Skin Test
The tuberculin skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is the most common method doctors use to test if you have TB in your body. This test requires you to have two visits with your healthcare provider.
On the first visit, the healthcare provider will inject tuberculin under the top layer of the skin of your forearm. A small, pale bump will then appear at the site of the injection.
The second visit always occurs after 48 hours and up to 72 hours. During this visit, your healthcare provider checks the injection site for any reaction. A hard and raised bump may indicate a positive TB infection, depending on its size and your medical history.
No reaction at the injection site means you have a negative TB test. Your healthcare provider will sometimes repeat the skin test a second time. This is known as a two-step TB skin test. Your doctor uses it to confirm that the result of your first test was not a false negative result.
Further testing is often recommended to confirm if you have a TB infection since a skin test may be flawed. Also, if you had previously received a BCG vaccine for tuberculosis, this could trigger a false positive result on your TB skin test.
Now, how does this compare to blood tests for TB?
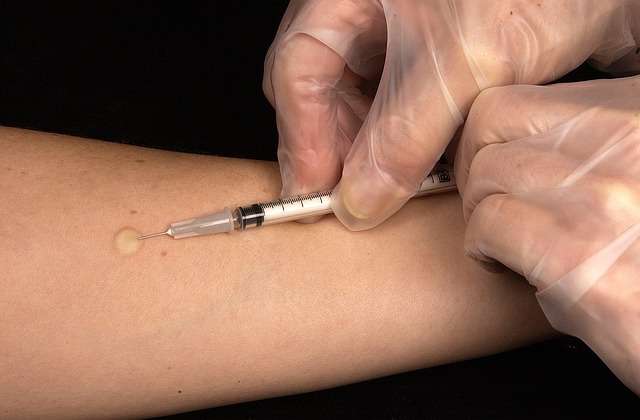
Quantiferon Blood Test
A TB blood test, also known as the interferon Gamma Release Assay (IGRA), detects if you have TB bacteria. One TB blood test approved by the FDA is the Quantiferon Gold Plus blood test.
During this test, a healthcare provider draws blood and then sends it to the laboratory for analysis and results. A positive blood test means that you have been infected with the TB bacteria, while a negative result indicates no evidence of the disease was detected. Your doctor will recommend additional tests like a sputum culture or an x-ray to confirm if you have latent or active TB.
A Quantiferon Gold Plus blood test is convenient compared to a skin test for the following reasons:
- It only requires one single visit.
- Your test results are typically available between three and five business days.
- It's unaffected by the BCG vaccine. Therefore, the results are less likely to return as false-positive.
- Results are not affected by provider bias.
If you need to get tested for TB but you're not sure which test is right for you, talk to your healthcare provider!
Need TB testing? eNational Testing can help.
What is TB?
Tuberculosis is a highly infectious disease that typically attacks the lungs. The bacteria that causes TB is known as mycobacterium tuberculosis and spreads from one person to another through the air.
There are two types of TB: latent TB and active TB (TB disease).
Latent TB
Latent TB means that at some point in the recent or distant past, you were exposed to someone who had active TB. TB bacteria are present in your body when you have this type of TB, but you won't show any symptoms or feel sick. You will test positive with both methods (skin and blood).
The immune system fights and prevents TB bacteria present in the body from growing.
People with latent TB can't spread the disease to others. Even though the individual will feel normal, it's recommended for people diagnosed with latent TB to receive treatment as it helps prevent the infection from becoming an active disease.
Active TB
This is a type of TB where the bacteria are actively multiplying in your body. People with active TB show symptoms, become sick, and can spread the disease to other people. In this case, it is crucial (and required by public health) to receive prompt treatment.
When Should You Get a TB Test?
You might need a TB test if you show TB symptoms or are at a high risk of infection. Some institutions will also require you to get a tuberculosis test for you to work there.
How will you know if you potentially have TB? The following are some of the more common symptoms:
- Cough that produces phlegm.
- Cough that lasts for several weeks.
- Unintentional Weight loss.
- Unexplained Fatigue.
- Unexplained Loss of appetite.
- Night sweats.
You are at high risk of getting TB if you:
- Have been exposed to someone with active TB.
- Have a medical condition that weakens your immune system.
- Are working in a correctional facility.
- Are a healthcare worker.
- Have traveled to a country where TB is common.
- Inject illegal drugs.
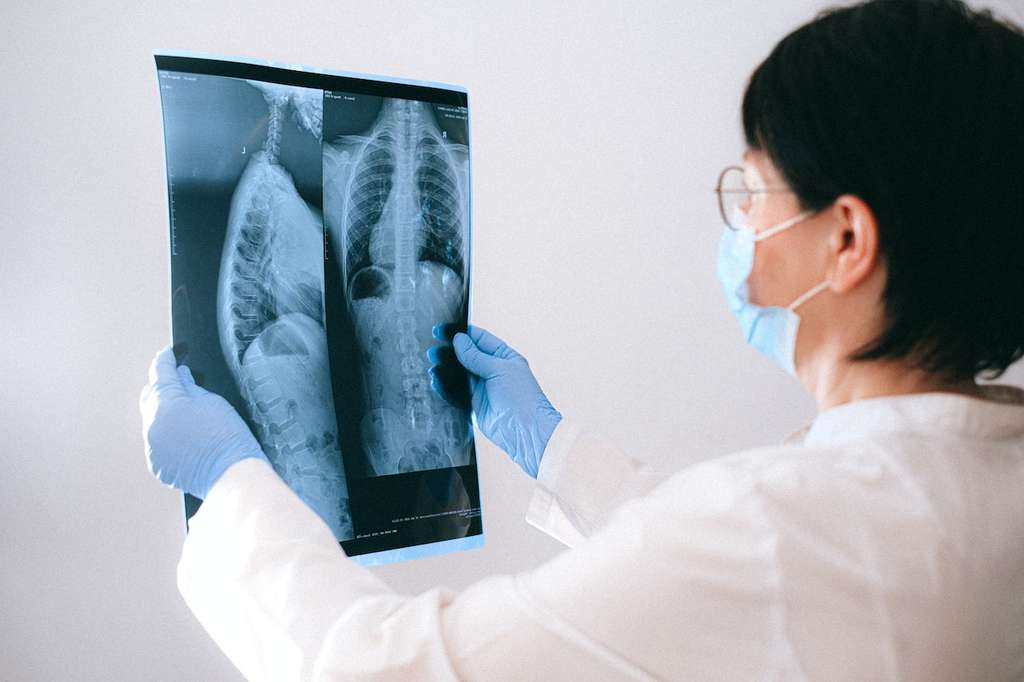
What Happens if You Test Positive for TB?
A positive TB test indicates you have probably been exposed to the TB bacteria. Your healthcare provider will likely order more tests to confirm the bacteria's presence and help make a diagnosis. You might need to receive an imaging test or a sputum culture.
Imaging Test
A provider may order a CT scan or a chest x-ray after a positive test. These tests help the provider confirm TB's presence by showing images of the lungs. It might show changes in the lungs caused by active TB.
Sputum Culture
Sputum is the mucus that comes up after you cough. Providers use it to test the different strains of TB. The test result helps the provider choose the best treatment.
After confirming the presence of tuberculosis bacteria, the provider may recommend antibiotics if you have latent TB. A combination of different drugs is prescribed if you have active TB and should be taken for four to nine months without fail.
TB testing is essential for public health. Go for a TB test if you start developing common symptoms or if you are at a high risk of contracting TB. e7 Health offers both skin testing and blood tests. Schedule your appointment online today!

OMG, so e7 is one-of-a-kind in Vegas. My husband needed a TB Skin Test and I was able to book for the next hour. The staff actually answers the phone, right away. They are kind and nice. Upon arrival, at e7 Windmill location, the receptionist (who's name I do not have) was so kind, nice, and caring. She's a gem. During our brief wait for my husband's appointment, I witnessed the interaction between staff members and also, their clients. It's amazing that the entire, big e7 Team loves each other and what they do. You do not see this anywhere else. The team's interaction was magical. AND then how each staff member interacts with their patient, well... just unique. My husband had Alia, who definitely folded her Angel Wings in to fit in to the treatment room. What an amazing being. So patient, as my husband was on a walker and not so ambulatory. She explained all so clearly and easily. Truly, we have never experienced such CARE not just in Vegas, but anywhere. She also went above-and-beyond for us as to the next step. e7 scared me at first online, but now, they are my Go To and I have already recommended to many. God bless Alia and all. The Team truly LOVE what they do and it shows.
Read More

















